Every year more than 12 million people are diagnosed with cancer worldwide and over 7.5 million people die from cancer each year. These numbers are expected to increase because of population growth and due to the lifestyle in the Western world.
Radiotherapy is an important part of modern cancer treatment and more than 50% of cancer patients receive radiotherapy at least once. Modern radiotherapy relies on advanced high precision planning, treatment equipment and imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT), positron-emission tomography (PET) and magnetic imaging resonance (MRI) in order to deliver high radiation doses to a precisely defined target in patients. One of the main difficulties in external beam radiotherapy is that both tumors and the surrounding tissue move significantly and unpredictably during radiotherapy which complicates the delivery of high radiation doses to a precisely defined target. One way of minimizing this problem is the implantation of markers in or adjacent to the tumor allowing frequent imaging and treatment adaptation.
The DTU Center for Nanomedicine and Theranostics focuses on developing novel tissue markers based on gold nanoparticles for both local- and systemic administration. By co-formulating gold nanoparticles and hydrogel forming polymer suspensions, tissue markers can be inserted by parenteral injection using thin hypodermal needles (Figure 1). Additionally, methods to install tissue markers by systemic administration are currently under development. By exploiting the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect observed in solid tumors, long circulating gold nanoparticles can extravasate from the blood stream and accumulate in tumor tissue and thereby by function as an ideal tissue marker. Such tissue markers may subsequently be used to precisely locate the tumor in patients during treatment thereby improve the accuracy of the radiation dose given and reduce the exposure of healthy tissue during radiation. DTU established a spinout company in 2010, Nanovi, and are moving this technology towards clinical trials and market.
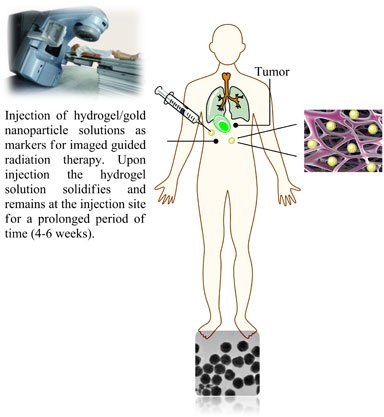
Figure 1 Parenteral injection of hydrogel/gold nanoparticle suspensions allows easy installation of tissue markers which can be used for frequent imaging and treatment adaptation for image guided radiation therapy, thereby improving the accuracy of the radiation treatment.
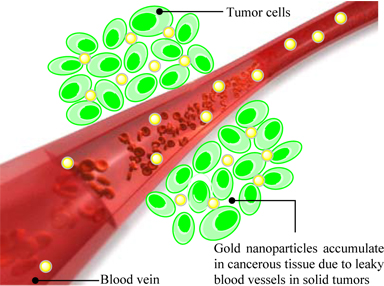
Figure 2 Long circulating gold nanoparticles extravasate from the blood stream and accumulate in tumor tissue due to the EPR-effect. The enhanced accumulation of gold nanoparticles in cancerous tissue may subsequently be used as reference markers for precise localization of the tumor in patients during radiation therapy, thereby improving treatment efficiency and reducing side effects due to radiation of healthy tissue.